
For example, a lithium atom (Z=3, A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7 – 3 = 4).Ī molecule is a chemically bonded group of two or more electrically neutral atoms. Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), it is easy to find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. The list below illustrates the charges and the masses of the subatomic particles: Scientists determine the atomic mass by calculating the mean of the mass numbers for its naturally-occurring isotopes.

Electrons are much smaller in mass than protons, only about 1/1800 of an atomic mass unit, so they do not contribute much to an element’s overall atomic mass. A single neutron or proton has a weight very close to 1 amu.

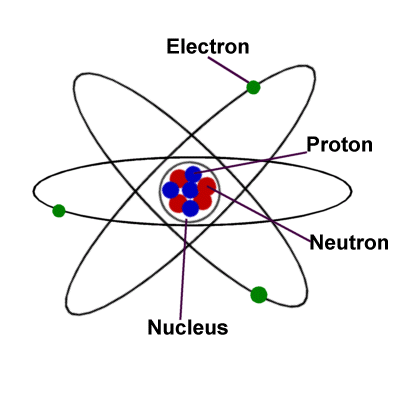
The observed atomic mass is roughly equal to the sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up the atom. In this scale 1 atomic mass unit (amu) corresponds to 1.660539040 × 10 −24 gram. It is expressed as a multiple of one-twelfth the mass of the carbon-12 atom, 1.992646547 × 10 −23 grams, which is assigned an atomic mass of 12 units. In simple terms, “atomic mass”, is the quantity of matter contained in an atom of an element. Atoms are the smallest units of matter that can participate in a chemical reaction involving solely atom rearrangement. Compound molecules are formed when atoms of one element interact with atoms of another element in a simple whole-number ratio.ĥ. A tiny number of atoms of an element unite to form molecules of the element.Ĥ. An element's atoms are identical in every way, including size, mass, density, and chemical characteristics, but they differ from atoms of other elements.ģ. Matter is made up of atoms, which are extremely small and indivisible particles that cannot be generated or destroyed.Ģ. Protons have a positive charge, while electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge.ĭalton's atomic theory has certain strange features:ġ. The nucleus usually has the same amount of protons and neutrons, collectively referred to as nucleons. The radius of an atom is usually measured in nanometres.Īn atom is made up of three particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons, with the exception of hydrogen, which has no neutrons.Įvery atom contains a nucleus that is surrounded by one or more electrons. However, assuming that the distance between neighbouring atoms is equal to half the radius of an atom, the size of an atom can be approximated. Because it's difficult to detect the positions of electrons surrounding the nucleus, measuring the size of an isolated atom is impossible. When more than millions of atoms are packed together, a layer of an atom the thickness of a thin sheet of paper is created. When an atom contains more or fewer electrons than protons, it has a negative or positive overall charge, and these atoms are known as ions.Īn atom is exceedingly small, much smaller than our imagination allows us to imagine. Like the layers of an anion, these electrons are organised in orbits around the nucleus of the atom. To have zero charge, an element's atom must have the same amount of protons as electrons. A single negative charge is carried by an electron. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus is used to calculate an element's atomic weight. The number of protons or positive charges in the nucleus determines an element's atomic number. A proton is a particle with a single positive charge and a mass of one unit. A neutron is a neutral particle with a mass of one unit. The nucleus is made up of neutrons and protons, which are responsible for an atom's weight and positive charges. The atom is electrically neutral if the number of protons and electrons is equal. Protons have a positive electric charge, while electrons have a negative charge and neutrons don't have any. The nucleus contains more than 99.94% of an atom's mass. Only one type of hydrogen, the most prevalent, lacks neutrons. One or more protons and a number of neutrons make up the nucleus. This article will study atoms, molecules and ions, the difference between atom and molecule and molecular elements in detail.Ītoms Molecules and Ions Atoms and Molecules DefinitionĮvery atom is made up of a nucleus and one or more electrons attached to it. Atoms are extremely small, measuring about 100 picometers in diameter. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is made up of neutral or ionised atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that makes up a chemical element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
